How to set up GCP for collection of data by / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation
You can acquire compute and storage resources from GCP with the platform by
- Setting up the primary GCP project for / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation collection
- Setting up a Service Account in GCP
- Entering credentials into / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation
The below guide walks through this process.
This setup can be automated using our GCP Automated Setup
Setting up the Primary Google Project for / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation collection
In order to set up the project for / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation collection you need to
- Enable the Cloud Build API for the project
- Define a bucket for the Primary GCP Project where images will be stored and imported into / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation.
Note - if you are importing from more than one Google project you will need to designate one of those projects as the Primary GCP Project and create a bucket in that project to enable collection across the multiple Google projects
The / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Role
To appropriately scope a service account for / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation to operate, creating a custom GCP role allows specifying individual permissions. To achieve this, navigate to the Role section under the IAM and Admin tab. Create a custom role and add the following permissions:
If you're deploying into GCP, the Terraform script provided by / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation should have already created this role for you, prefixed with myCadoResponseRole.
// Instance Acquisition
"cloudbuild.builds.get",
"cloudbuild.builds.create",
"compute.disks.get",
"compute.disks.use",
"compute.disks.list",
"compute.disks.useReadOnly",
"compute.globalOperations.get",
"compute.images.create",
"compute.instances.get",
"compute.instances.list",
"compute.images.delete",
"compute.images.get",
"compute.instances.getSerialPortOutput",
"compute.subnetworks.list",
"compute.subnetworks.get",
// Compute Management
"compute.disks.create",
"compute.disks.setLabels",
"compute.images.useReadOnly",
"compute.instances.attachDisk",
"compute.instances.create",
"compute.instances.delete",
"compute.instances.setLabels",
"compute.instances.setMetadata",
"compute.instances.setServiceAccount",
"compute.machineTypes.list",
"compute.machineTypes.get",
"compute.regions.get",
"compute.subnetworks.use",
"compute.subnetworks.useExternalIp",
"compute.networks.get",
"compute.networks.list",
"compute.zones.list",
"compute.zoneOperations.get",
// Platform Update
"compute.addresses.use",
"compute.instances.addAccessConfig",
"compute.instances.detachDisk",
"compute.instances.deleteAccessConfig",
// GKE Acquisition
"container.clusters.get",
"container.clusters.list",
"container.pods.exec",
"container.pods.get",
"container.pods.list",
// IAM & Authentication
"iam.serviceAccounts.actAs",
"iam.serviceAccounts.create",
"iam.serviceAccounts.enable",
"iam.serviceAccounts.get",
"iam.serviceAccounts.getAccessToken",
"iam.serviceAccounts.getIamPolicy",
"iam.serviceAccounts.implicitDelegation",
"iam.serviceAccounts.list",
"iam.serviceAccounts.signBlob",
// Project Management
"resourcemanager.projects.get",
"compute.projects.get",
// Secret Management
"secretmanager.versions.access",
"secretmanager.versions.add",
"secretmanager.secrets.create",
// Bucket Acquisition
"storage.buckets.get",
"storage.buckets.list",
"storage.objects.create",
"storage.objects.delete",
"storage.objects.get",
"storage.objects.list",
If you'll be wanting to use this Role across multiple projects, you can create it at the Organization level- this is required if you'll be wanting to acquire assets from multiple projects under one service account.
If deploying into GCP, this can be done easily if the Terraform-created role already exists by using the command:
gcloud iam roles describe CUSTOM_ROLE_ID --project=YOUR_PROJECT_ID --format=yaml > cado-organization-role.yaml
This will output the role to a yaml file, which can be edited to serve as a template for the new organization role. To edit the template for org use delete the 'name' and 'etag' sections, as these will be project specific, then use the command:
gcloud iam roles create CUSTOM_ORG_ROLE_ID --organization=YOUR_ORG_ID --file=cado-organization-role.yaml
Enabling the Cloud Build API for the project
To enable Cloud Build API for a Google project, see the documentation at https://console.cloud.google.com/cloud-build/.
Once Cloud Build is enabled, a principal for Compute Engine will have been created in 'IAM and Admin > IAM' called xxxxxxxxxxxx-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com, we also need this principal to have the custom role we created in the previous step 'Customer -> <role_name>'. Do this by editing the principal with the pen icon on the right and selecting the appropriate role.
Defining a bucket for the Primary GCP Project
Create a bucket in the project that will store the captured raw data from across all GCP projects. For more information https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/creating-buckets
Setting up a Service Account in Primary GCP Project
Next, you need to set up a Service Account in GCP. For information on how to do this more see:
- https://console.cloud.google.com/iam-admin/serviceaccounts
- https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/service-accounts
Required Access
Both the / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation service account and the service account for the Cloud API need the custom role's permissions 'Custom -> <role_name>' role:
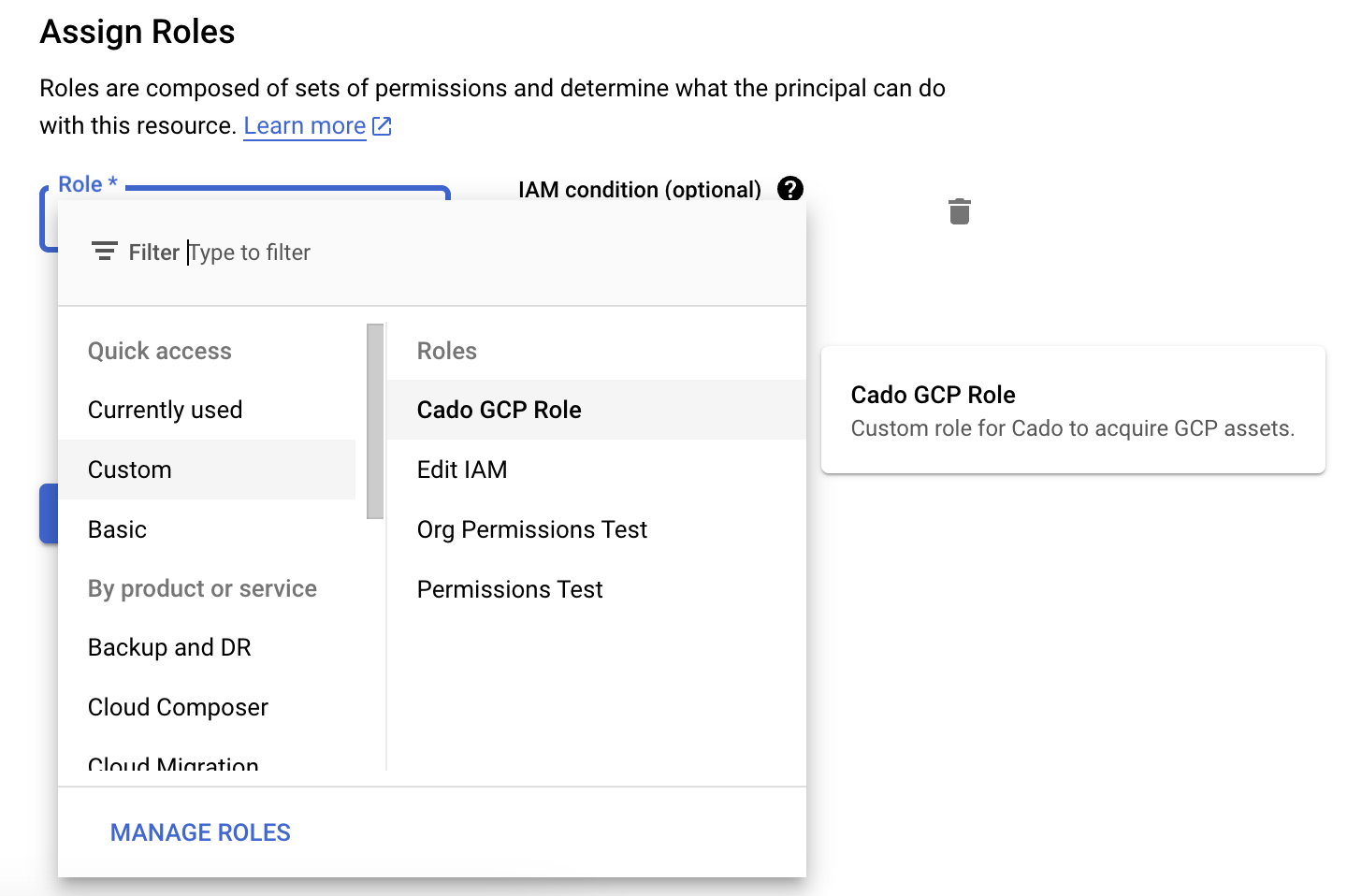
To import GKE containers, the / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation service account also needs the iam.serviceAccounts.implicitDelegation IAM permission.
Getting GCP Credentials
When you add credentials to Cado you are creating a mapping from a set of credentials (in GCP json format) to a project name.
Any time a user then attempts to access that particular GCP project name, the credentials that you registered in settings will be used. This keeps non-admin users from having to managing credentials themselves, while also allowing access to as many different GCP projects as you want.
There are two ways to achieve this:
- Service Account Credentials - this is a simpler but less secure approach. Note - / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation running in Azure only supports the use of Service Account Credentials
- Workload Identity Federation - This requires more expertise but is the recommended, more secure approach.
Service Account Credentials
The simplest method to add GCP credentials to / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation is to use a service account, which will give you a permanent key. These are very sensitive credentials but they are easy to manage and simple to set up. Adding GCP credentials for service accounts is supported by / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation when deployed in both AWS and Azure.
GCP credentials come in a json format that wraps around a ‘regular’ credential. It can be treated as functionally no different to how you would handle any type of password or key.
For example, a service account key would come in a structure such as the below. The ‘credential’ is a literal RSA key as a string in the private_key field, all other fields are metadata for the benefit of the application that uses it:
{ "type": "service_account", "project_id": "cool-project", "private_key_id": "22c14ac5b63...", "private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEvgIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKg...wggSkA.\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n", "client_email": "cool-project.iam.gserviceaccount.com", "client_id": "...", "auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth", "token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token", "auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs", "client_x509_cert_url": "..." }
Workload Identity Federation (Optional)
The GCP recommended best practice, is to use Workload Identity Federation, which allows credentials from another app to impersonate a GCP account. Note: / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation running in Azure does not support Workload Identity Federation credentials to import from GCP
Workload Identity Federation is more secure since the credentials are nothing but metadata telling the app where to go, while the validation is handled on the server side. Adding GCP credentials via Workload Identity Federation is currently only supported for / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation when deployed in AWS.
Rather than give out the key to a service account, you instead register the permission with GCP to allow AWS credentials for account 123 to act as if they were the given GCP service account.
You can download existing credentials by clicking the display name of the Identity Pool > Connected Service Accounts > Download, which will then ask you which identity’s credentials you would like to download.
For example:
{ "type": "external_account", "audience": "//iam.googleapis.com/projects/...", "subject_token_type": "urn:ietf:params:aws:token-type:aws4_request", "service_account_impersonation_url": "https://...ount.comgenerateAccessToken", "token_url": "https://sts.googleapis.com/v1/token", "credential_source": { "environment_id": "...", "region_url": "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/placement/availability-zone", "url": "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials", "regional_cred_verification_url": "https://sts.{region}.amazonaws.com?Action=GetCallerIdentity&Version=2011-06-15" } }
When setting up WIF credentials, we strongly recommend using the GCP Automated Setup scripts for ease of set-up.
For more information about GCP Workload Identity Federation see:
- https://console.cloud.google.com/iam-admin/workload-identity-pools
- https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/workload-identity-federation
Entering Settings
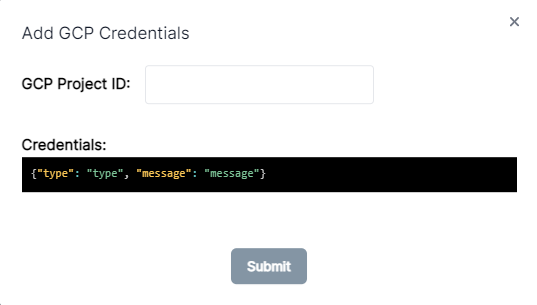
You can add GCP Credentials to / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation in the Settings > Cloud > GCP page. You will be asked for a "GCP Project Name" and the "GCP Credentials". These credentials will be a JSON either directly containing the service account credentials, or the Workload Identity Federation credentials
Collecting from multiple GCP Projects
After setting up your Primary GCP Project, to collect from multiple GCP projects follow the instructions in GCP Cross-Project Setup