How to Import Data from Kubernetes
How Does / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Import Data from EKS, ECS, AKS, and GKE?
When acquiring data from Kubernetes containers, / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation follows these steps by default:
- Executes a shell script to download the Host binary.
- Runs the binary to collect forensic artifacts.
- Uploads the collected files to cloud storage for processing.
The method used to execute the script depends on the environment. For example, ECS uses ECS execute, while EKS, AKS, and GKE use the Kubernetes control plane API, as explained here.
Authentication to the Kubernetes API may require IAM permissions, which are described in service-specific documentation.
Configuring the Cluster RBAC for Use with / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation
To acquire artifacts from a container, the following Kubernetes permissions must be enabled for each cluster:
pods-get,listpods/exec-create,get
RBAC ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding
We recommend adding the following ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding to your cluster’s RBAC configuration with the permissions listed above.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cado-eks-cluster-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/exec"]
verbs: ["create", "get"]
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cado-eks-cluster-role-binding
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: cado
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cado-eks-cluster-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Alternate Collection by Acquiring the Volume of the Node
If executing code inside the container or connecting over the network is not possible, you can acquire the volume of the node running the container. For example, this approach works for EKS running on EC2 nodes.
- If using the Docker container runtime, container file systems are usually available at
/var/lib/docker/overlay2. - If using the Containerd runtime (which is now the default for EKS), the container file system is not immediately visible. / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation is working on supporting containerd-based volume acquisitions.
Alternate Collection by Using Host with a Sidecar Container
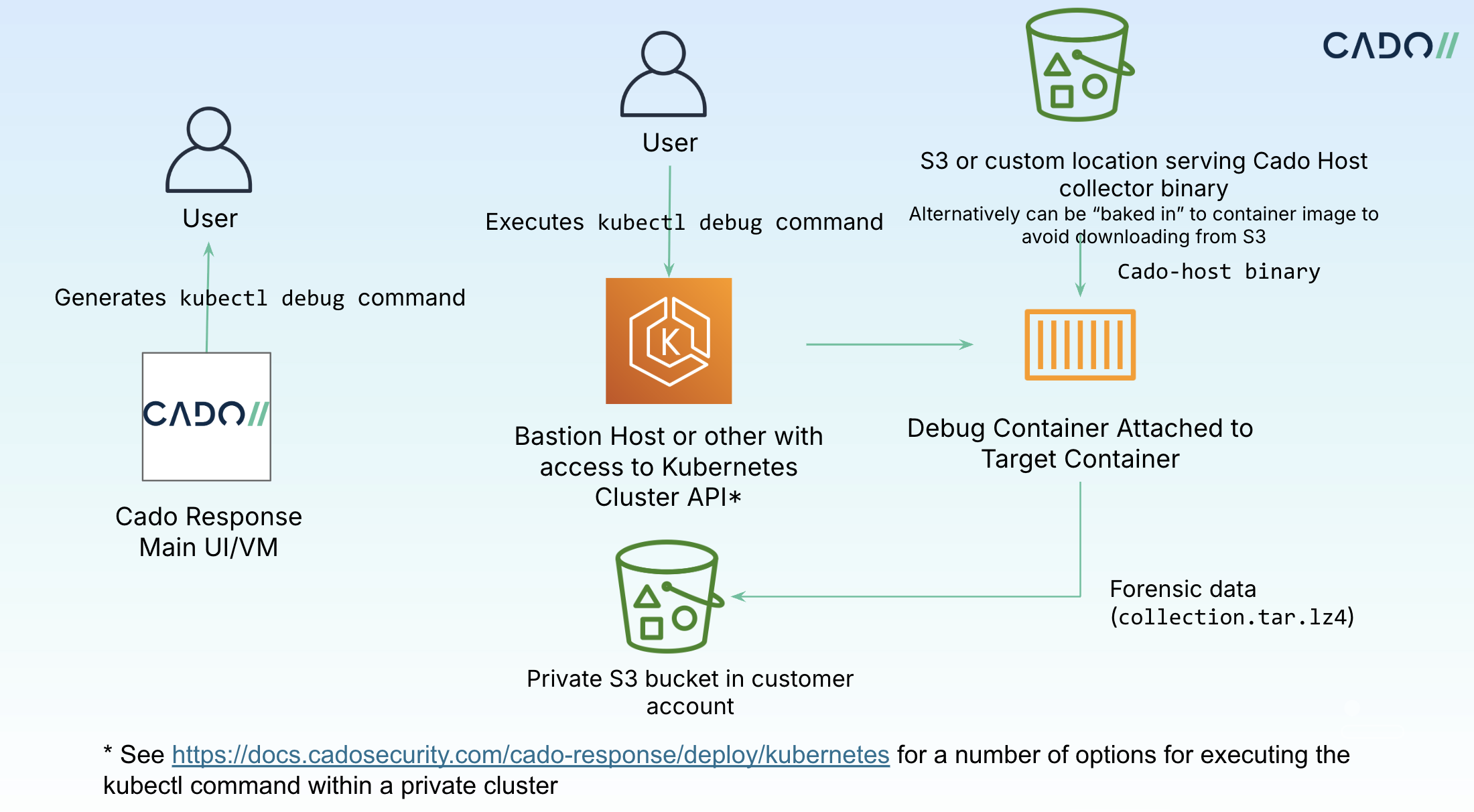
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation supports collecting from private clusters and distroless containers by using a debug container.
To acquire data:
- Navigate to Import > / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host.
- Select Kubernetes and follow the prompts.
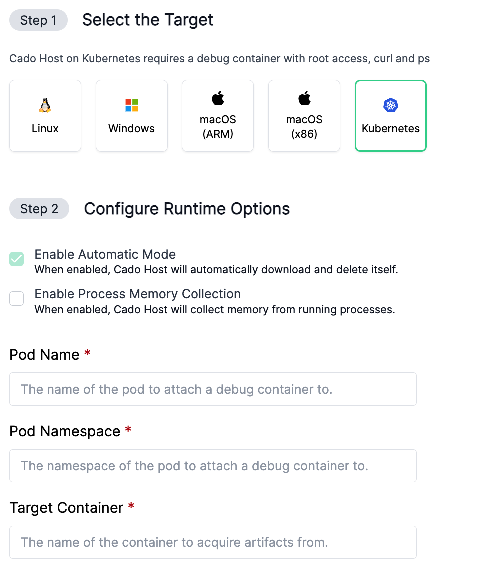
This will use a command such as the following to start a debug container and execute / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host:
kubectl debug -it pod-name --image=debian:latest --target=target-container -n pod-namespace -- sh -c
The diagram below provides a high-level overview of how this works:
Using a Custom Image
In environments where the default debian:latest image is not supported, you can use a custom image. The custom image must have the latest / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host Linux binary located at /tmp/cado-host-static/cado-host. However, / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation recommends using the default debian:latest image for supportability.
Root Access
By default, / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host requires root access to access the underlying container file system (usually under /proc/{PID}/root). The runuser command with the root user is also required to give the / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host process the appropriate UID and GID.
For Kubernetes v1.30 or later, you can optionally use the "Run as non-root user" option, which leverages the sysadmin profile to access the container file system.
Private Clusters with No Network Access
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation requires access to the Kubernetes control plane API to acquire containers via the user interface. If network access to the Kubernetes API is not available, alternate options for acquiring data are needed.
Private AKS Clusters
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation can acquire private AKS clusters using the normal user interface, thanks to Azure's "command invoke" feature for private clusters.
Private GKE Clusters
Please use the Alternate Private Cluster Access with a Sidecar method described above.
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation is exploring support for private GKE clusters through public endpoints on private clusters via the "normal" method.
Private EKS Clusters
If the / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation platform does not have access to the cluster endpoint, you can acquire data by deploying the Host/Sidecar acquisition script.
To do this, connect to your EKS cluster using a command like:
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region $Region --name $ClusterName
Follow AWS’s instructions here.
Then execute the kubectl script generated at Import > / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host > Kubernetes.
Methods for Executing Kubernetes API Commands Inside a Private Cluster VPC
If the cluster is configured with "Private endpoint only," you will need to use a method like VPC peering or another connection option to access the API to start the sidecar. How to implement this will be dependant upon your Kubernetes deployment.
Various methods can be used to access the Kubernetes API in a private VPC, including:
- Bastion Hosts
- SSM (AWS Systems Manager)
- AWS PrivateLink
- AWS Cloud9
- VPN/Direct Connect
For details on these methods, refer to the following resources:
-
Bastion Hosts:
-
SSM:
-
VPN/Direct Connect:
-
PrivateLink:
-
Cloud9: