How to Collect Process Memory with / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation
You can perform a memory acquisition of a Windows or Linux system using Cado Host by navigating to Import > / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host within the platform and running the pre-generated script on the host device. For detailed instructions, see here. Note that process memory collection is not currently supported on macOS.
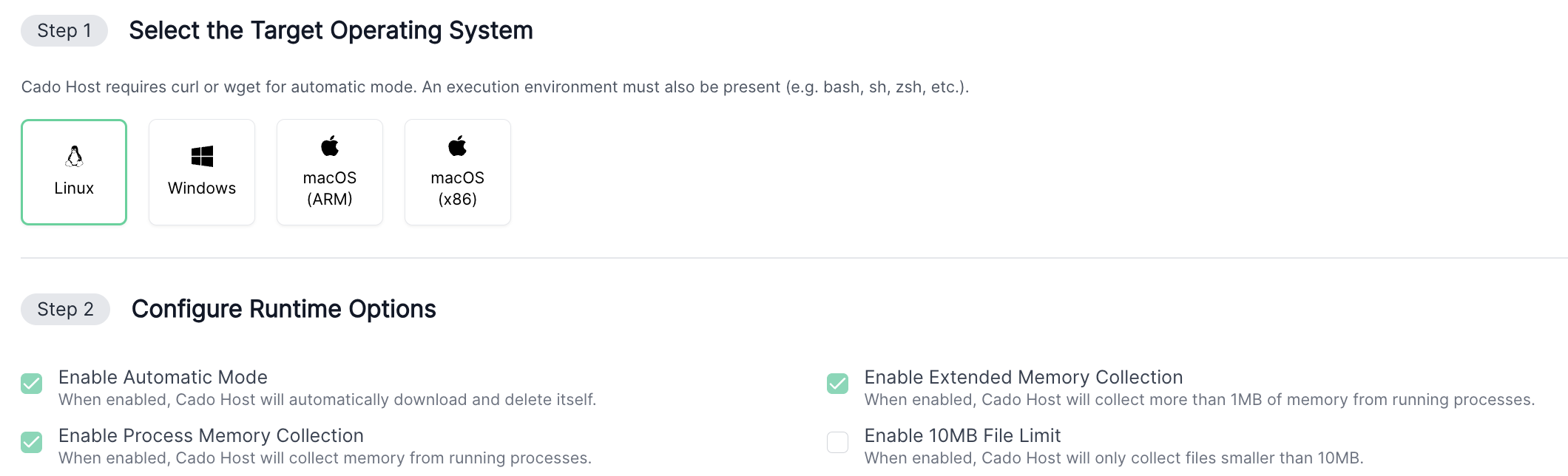
Enabling Memory Collection
In the console and within Host, make sure to enable the options to collect memory. You can also optionally enable Extended Memory Collection to capture larger process memory files, particularly useful on Windows systems, although this can slow down the collection process.
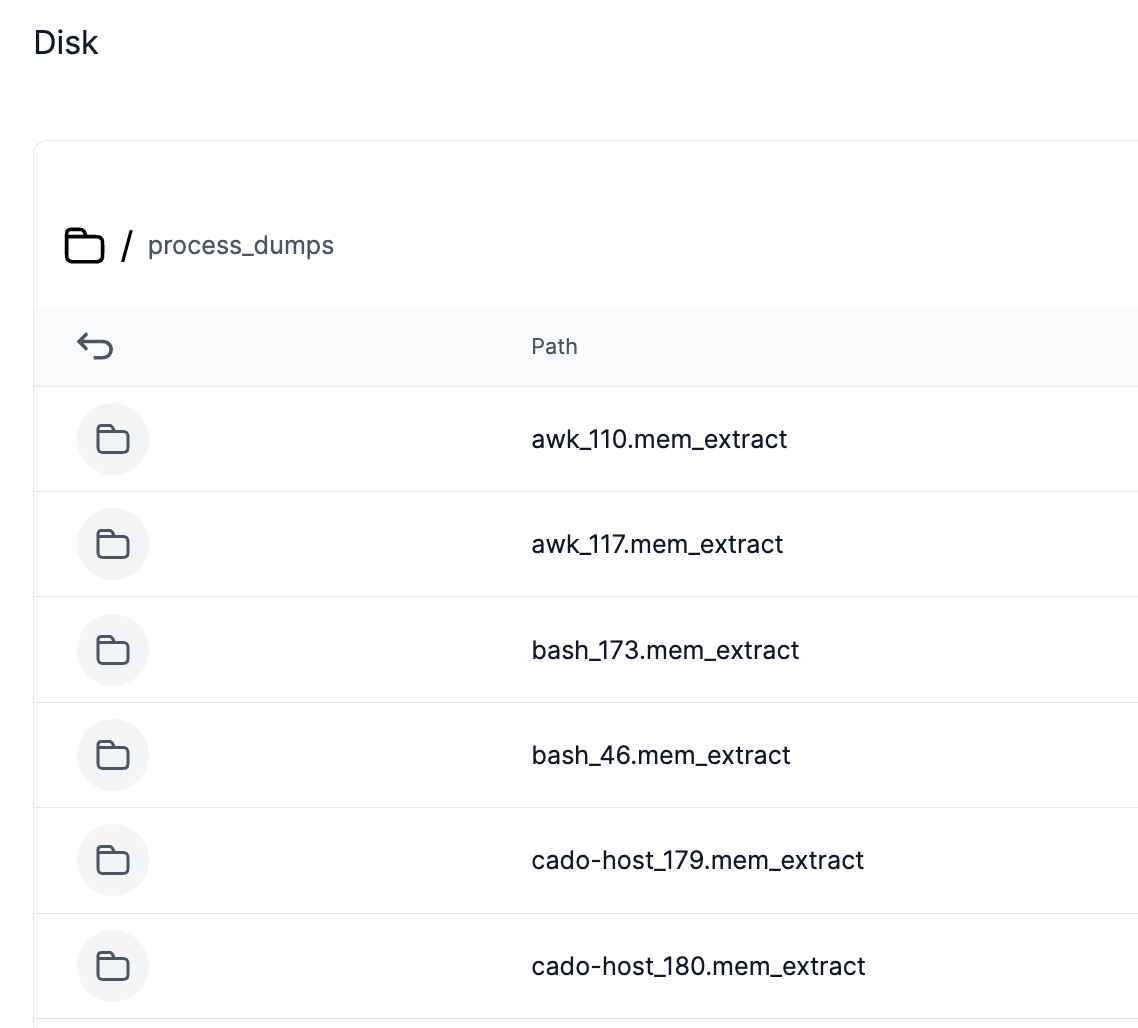
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation collects memory from individual processes as .mem files, which can be found in the "process_dumps" folder. This method provides more reliable analysis compared to older versions, using the / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation branded open-source tool varc.
Acquiring Memory from AWS EC2
To acquire memory from Linux systems in EC2, use the Alternate Acquisition option under Import > EC2:
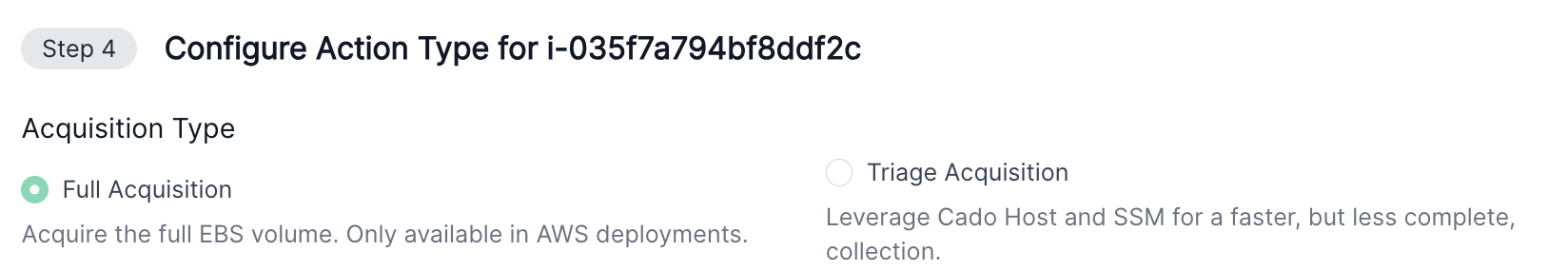
This requires that the AWS SSM agent is running on the EC2 instance and registered within AWS Systems Manager. If the SSM agent is not available, you can still acquire memory by connecting to the machine via SSH or RDP and running Host from Import > Host. This method also works for Windows systems.
Collecting Memory from Containers
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation will attempt to collect memory from containers (e.g., ECS, EKS, AKS) by default. Some specifics from our testing:
- AWS Lambda: Successfully dumps process memory by default, but requires manual execution within the Lambda function.
- EKS on EC2: Successfully dumps process memory by default.
- ECS on Fargate: Requires enabling
CAP_SYS_PTRACEin the task definition to collect process memory.
Processed Memory
Once the memory collection is complete, you can browse the file system through the / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation UI, view file contents that were in memory at the time, and analyze information on running processes and network connections.
-
Collected memory files are stored in the "process_dumps" folder:
-
Running process information is stored in
processes.json: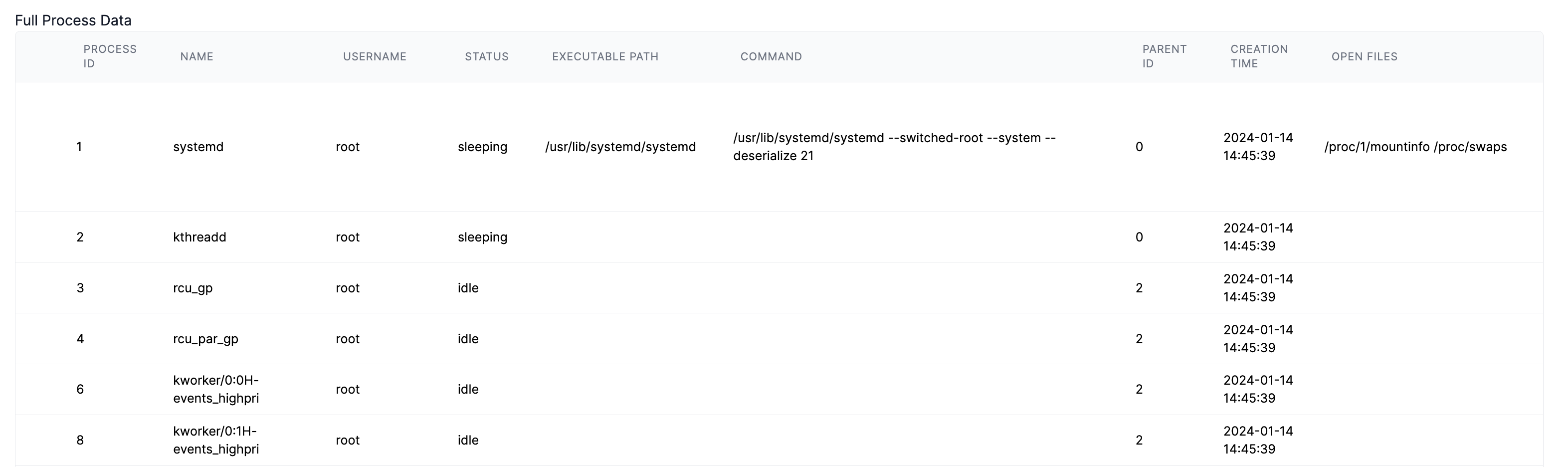
-
Network connections are recorded in
network.json, open files inopen_files.json, and files collected from memory are stored in thecollected_filesfolder.