AWS EC2 Run Command
/ Forensic Acquisition and Investigation allows you to execute scripts on target systems using the Run Command feature in the import wizard.
This requires the AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM) to be installed on the instance and admin privileges within / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation. To support transferring of files over the SSM port forwarding, we require Python 3.8+ to be installed on the instance.
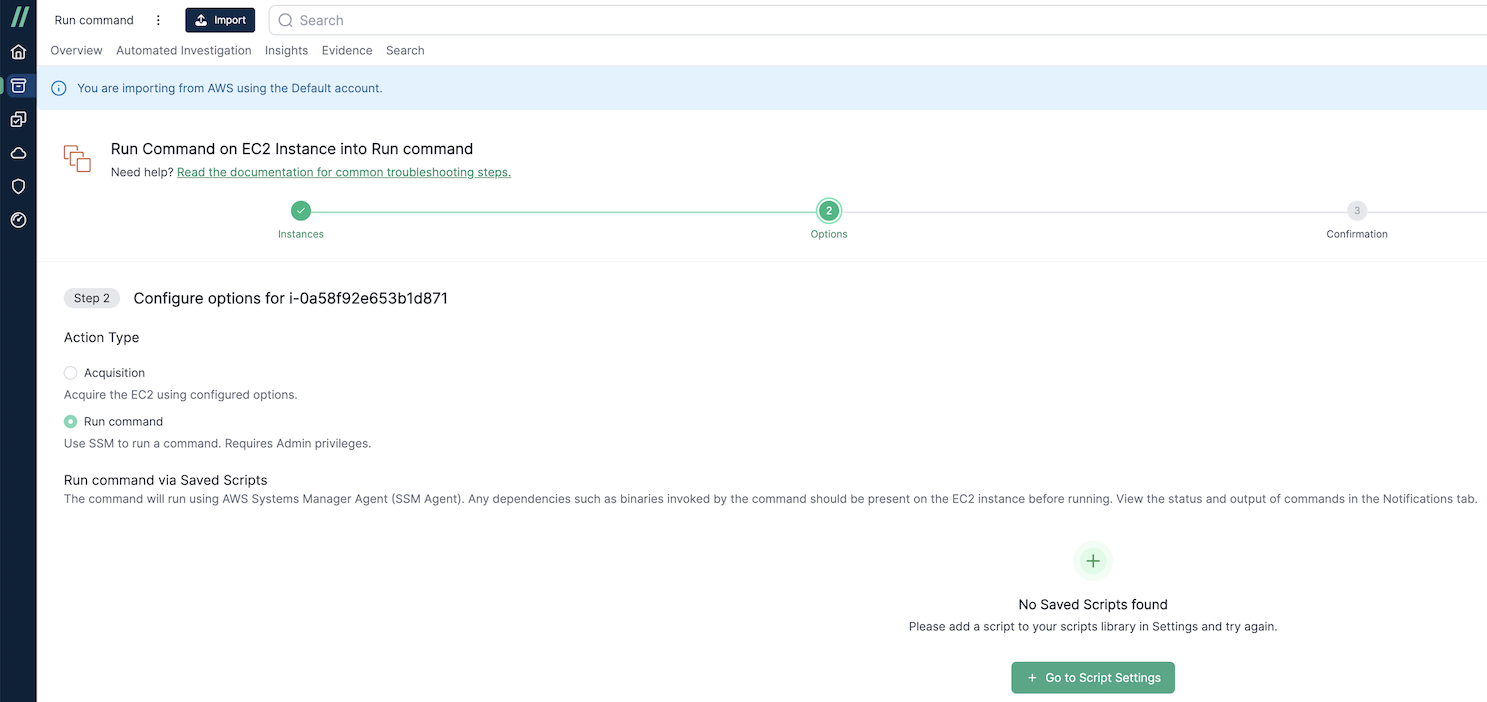
To use this feature, you must create a script at Settings > Scripts.
For more information on the AWS IAM permissions for SSM required, please see here.
Note: This feature is in Beta. To enable it, go to Settings > Experiments > Run Action.
Creating a Saved Script
- Go to /settings/scripts and click Create Script.
- Choose whether the script will run on Linux or Windows (reduced functionality for Windows). For this example, we’ll choose Linux.
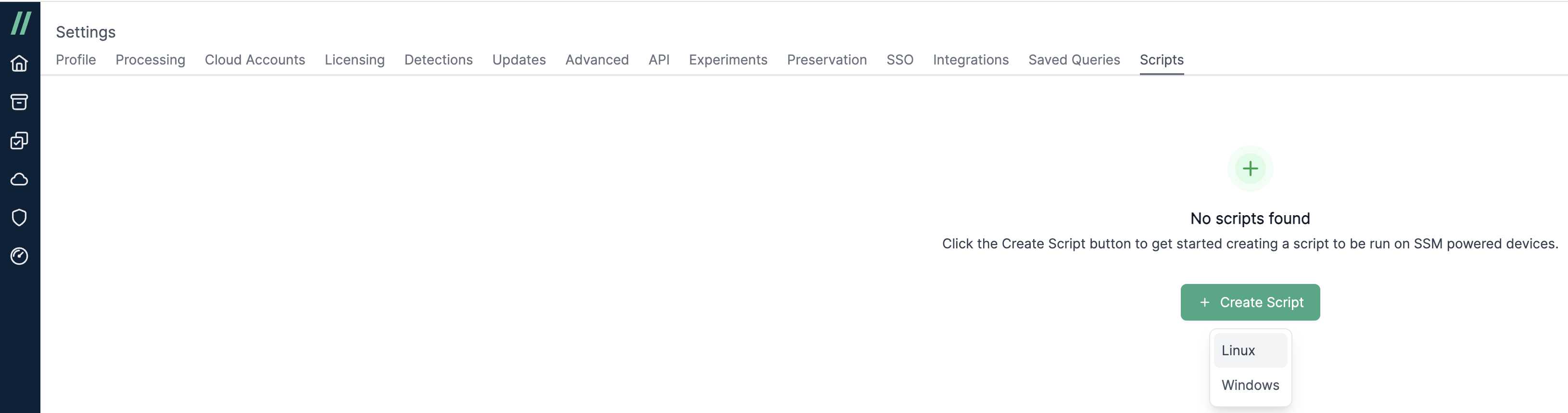
- In Step 1, provide a Name and Description for the script.
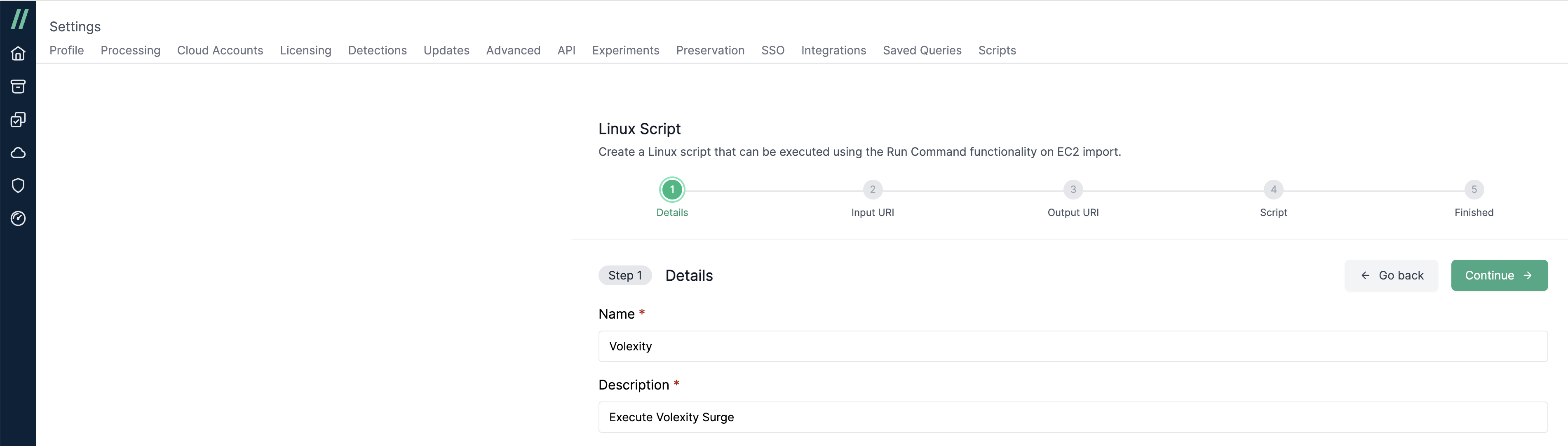
- In Step 2, provide the location of the input file (valid S3 URI), which will be downloaded onto the target system. This step is not available for Windows scripts.
- In Step 3, specify the location of the output file on the target system that will be uploaded to your / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation S3 bucket. This step is not available for Windows scripts.
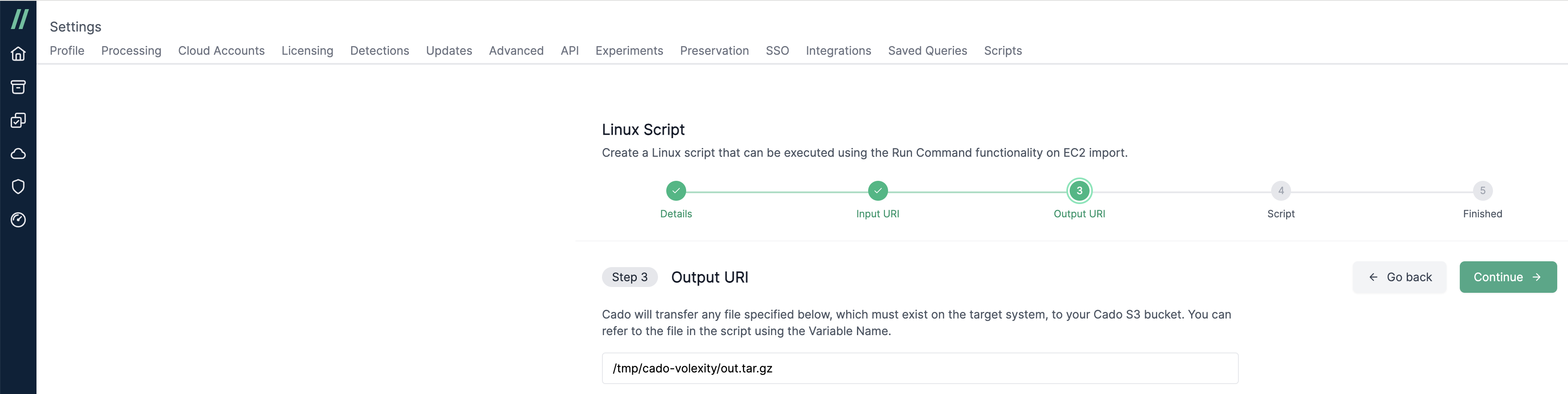
- In Step 4, paste the script that will run on the target system. The input and output files can be referenced as
${INPUT}and${OUTPUT}respectively. Windows scripts do not require these variables.
Example script for Volexity Surge Collect:
mkdir -p /tmp/cado-volexity
cp ${INPUT} /tmp/cado-volexity/surge-collect
chmod 755 /tmp/cado-volexity/surge-collect
mkdir -p /tmp/cado-volexity/out
/tmp/cado-volexity/surge-collect $password --format=zip --pagefiles temp_out
find temp_out -type f -name '*.zip' -exec mv {} ${OUTPUT} \;
(sleep 30; rm -rf /tmp/cado-volexity) &
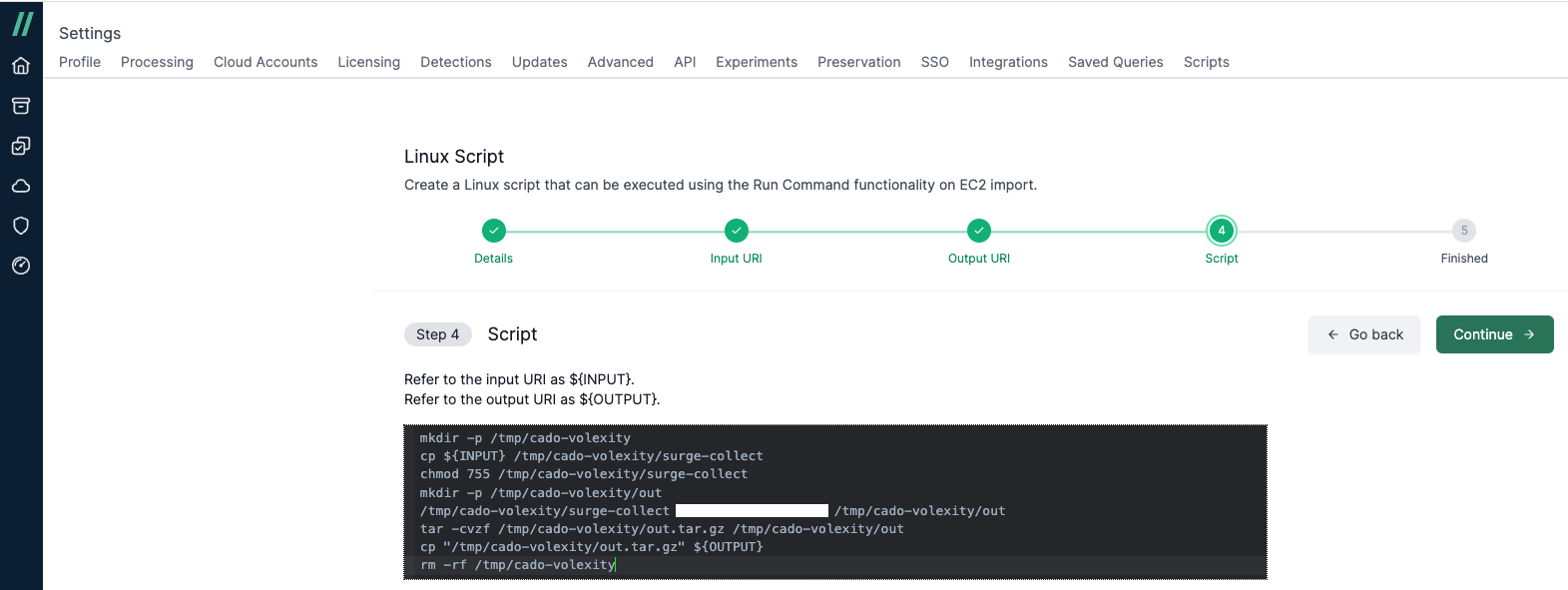
- Click Continue and you’ll see your script listed in the scripts table.
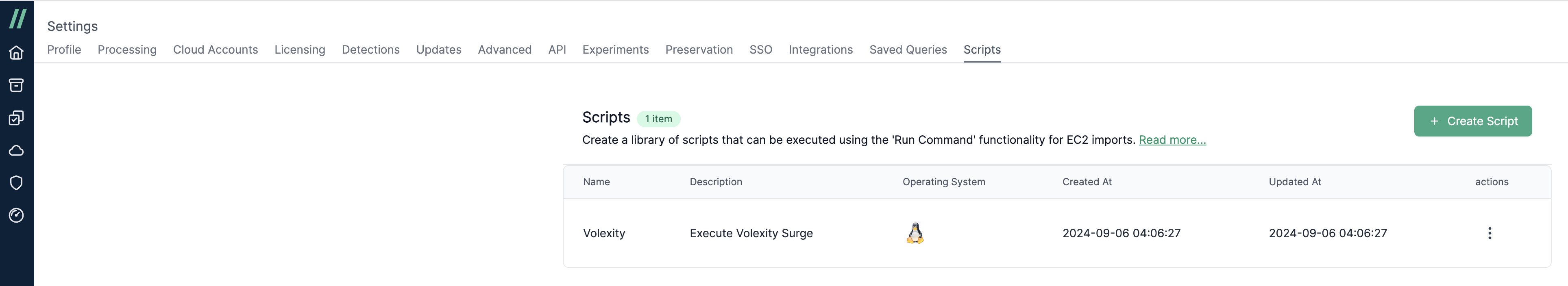
Running the Script
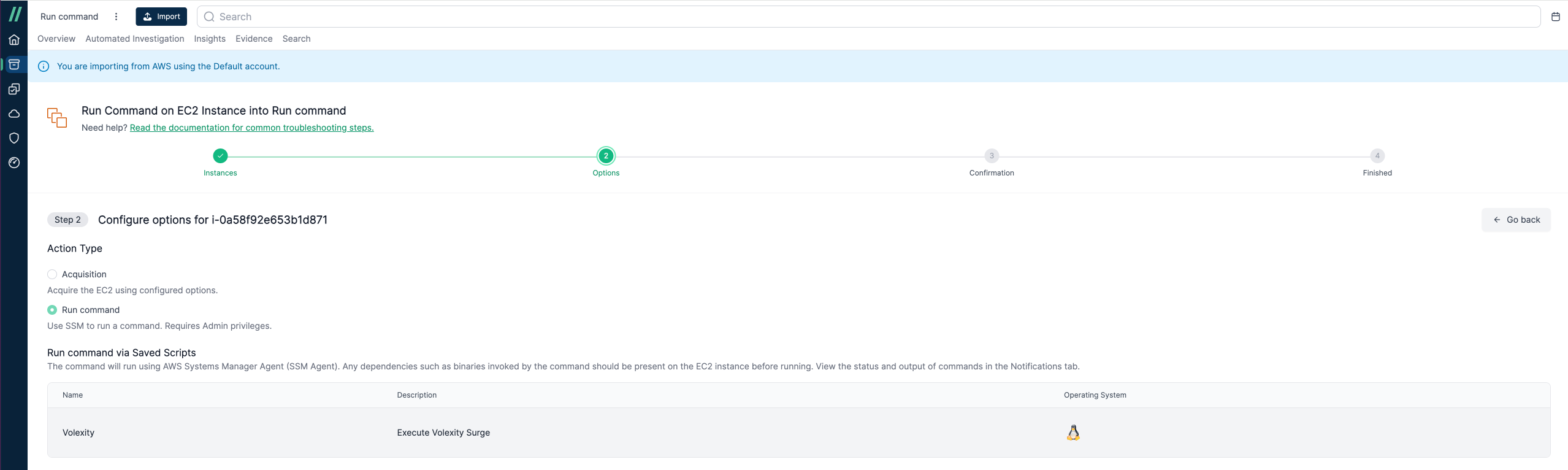
Use the Import Wizard to select an EC2 instance with the SSM agent installed. Choose Run Command as the action type, and you’ll see the script created earlier. Complete the import as usual.
How does the Run Command feature work?
When you execute a saved script via Run Command, / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation leverages AWS Systems Manager (SSM) to remotely execute your script on the target EC2.
-
Preparation and Validation
- Platform Verification: The process begins by verifying that the target instance is a Linux system.
- Script Selection: The command will either use a pre-saved script you have created from your / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation settings, or the script used to import through / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation Host.
- Port Selection: A specific port (by default, the SSM port 9999) is used to establish the port forwarding session between your local worker and the target instance.
-
Input File Handling
- Downloading the Input File: If your script requires an input file (specified as an S3 URI or a designated / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation host URL), the file is first downloaded to a temporary location on the main / Forensic Acquisition and Investigation instance.
- Transferring to the Instance: Once the input file is available locally, it is transferred securely to the target EC2 instance over the SSM port forwarding session.
-
Command Execution on the EC2 Instance
- File Path Substitution: The command is automatically updated so that the placeholders for the input and output files (
${INPUT}and${OUTPUT}) point to the temporary file locations on the target instance - as per the examples above. - Remote Execution: The command is then executed on the target instance via SSM. During execution, the script reads the transferred input file and writes its results to an output file on the instance.
- File Path Substitution: The command is automatically updated so that the placeholders for the input and output files (
-
Retrieving the Output File
- Downloading the Output File: After the command has executed successfully, the system retrieves the output file from the instance using the same SSM port forwarding mechanism.
- Uploading to S3: Once the output file is securely transferred back to the controlling system, it is automatically uploaded to your designated Cado S3 bucket.
-
Cleanup
- Instance Cleanup: To maintain a clean environment, temporary files on the target instance (such as the transferred output file) are removed after the successful upload to S3. Any process running on the port forwarding session is also terminated, determined by the port number used.